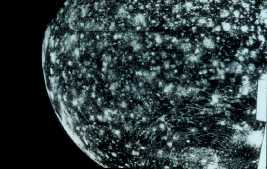
This image shows the varied terrain of Ganymede.
Click on image for full size
NASA
Surface of Ganymede
The surface of Ganymede is halfway between that of
Callisto and that of
Europa. Portions of the crust are of ancient age, while other portions are relatively
new.
The little white dots shown in this image are the many imact craters on Ganymede. Portions of Ganymede that are heavily cratered have not been resurfaced, indicating that they are of ancient age.
Besides the craters, the surface of Ganymede is made of grooved terrain, light terrain, and dark terrain.
Because many different kinds of terrain can be found on the surface of Ganymede, some processes of change in the interior must have taken place during Ganymede's history.
You might also be interested in:
The surface of Callisto is deeply pockmarked with craters. It looks to be perhaps the most severely cratered body in the solar system. There are also very large craters to be found there. The severity
...more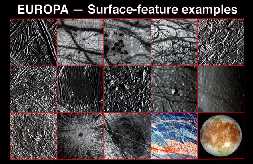
The picture to the left shows examples of the many amazing different surface features of Europa. Many exciting discoveries were made about Europa during the Galileo mission. The surface of Europa is unusual,
...more
There has been no icy volcanism on Ganymede, nor continental drift, but it does seem that there have been movements of the surface. Examination of the surface of Ganymede reveals many kinds of faulting.
...more
This image shows an example of the grooved terrain of Ganymede. The image clearly shows that some things hit Ganymede and made craters after the grooves were made, because the grooves are underneath the
...more
This image shows an example of the light terrain of Ganymede. The image shows the contrast between the light terrain and the dark terrain of Ganymede. The light terrain is where the grooves of Ganymede
...more
The diagram to the left shows a cutaway of the possible inside structure of Ganymede, based on recent measurements by the Galileo spacecraft. It shows a small core of metal, overlain with some rocky material,
...more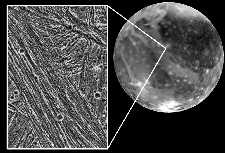
Instead of icy-volcanism, the surface of Ganymede reveals gradual surface deformation and stretching, a stretching similar to the crustal deformation of the Earth. In this case, the folding and stretching
...more















