This image shows the Rover at work.
Click on image for full size
Image from: JPL/NASA
Soils explored by the Rover
Spinning the Rover's rear wheels was one way for scientists to test the soil of Mars. As the wheels dug into the surface, the Rover discovered that much of the ground is made of dust, possibly deposited during many of the Martian Global Dust Storms.
Everywhere the Rover passed, it disturbed the soil, and the soil underneath turned out to be a darker red-brown soil than it's surroundings. An example of disturbed soil occured when the Rover crossed the Mermaid Dune, shown here.
Soils found by the Pathfinder's Rover seem to be different from those soils found at the Viking landing sites. Soil found around the rock the Lamb may even show that Mars had to have more water in the past!
You might also be interested in:

This image shows the rock called Pooh Bear. Soil found near Pooh Bear seemed to be a clumpy kind, made of little fine grains and cloddy. This was different from the soils found near the rock Scooby Doo,
...more
People were really excited when Pathfinder landed on Mars on July 4, 1997. The Mars Pathfinder mission (MPF for short!) was sent to Mars to look at the rocks and soil of Mars. The MPF was actually 2 parts,
...more
The Viking I and Viking 2 missions were to both orbit Mars and land on the planet's surface. There were two spacecraft for each mission. At this stage in the history of the exploration of Mars, scientists
...more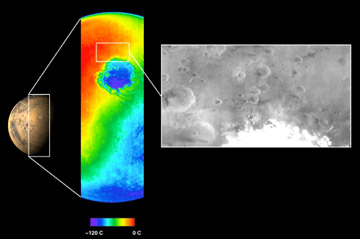
The Mars Odyssey was launched April 7, 2001. After a six-month journey, the Odyssey arrived at Mars on October 24, 2001. The instruments onboard the Mars Odyssey will study the minerals on the surface
...more
The Mars 2005 mission is still in the planning stages. It is set to launch in the year 2005.
...more
Aerobraking slowed the Mars Global Surveyor down when it reached Mars. Aerobraking also helped MGS to get into the right orbit for mapping the surface of Mars. Aerobraking means that the MGS flew through
...more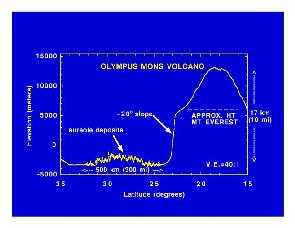
Mars Global Surveyor carries an instrument which measures the heights of things. This instrument is called an altimeter, or "altitude-meter". The graph to the left shows the results returned from Mars
...more















