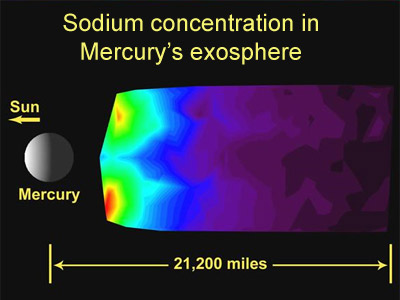
Mercury's tenuous atmosphere (exosphere) contains hydrogen, helium, and oxygen, as well as smaller amounts of sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. This graphic shows sodium concentration near Mercury as detected by the MESSENGER spacecraft in October 2008.
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington.
Atmosphere of Mercury
Mercury has very little atmosphere. The planet's small size means that its gravity is too weak to hold down a normal atmosphere. There is a very thin atmosphere around the planet. Mercury's thin atmosphere is constantly being "blown away" into space by the pressure of sunlight and by the solar wind. The tiny planet's atmosphere is also constantly replenished.
Mercury's atmosphere contains small amounts of hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. It also has even tinier quantities of sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. Hydrogen and helium come from the solar wind. Helium, sodium, and potassium are produced by radioactive decay in Mercury's crust. Micrometeorites vaporize surface rocks, adding gaseous sodium, potassium, and calcium to the thin, exotic "air". All of these gases are soon ionized by heat, sunlight, or radiation, and are quickly carried away from Mercury by the solar wind and interactions with Mercury's magnetic field. Atmospheric pressure at the planet's surface is less than one trillionth of Earth's (around one nanopascal or 10-14 bar).
Temperatures at the surface range between 100 and 700 kelvins (-280° F to 800° F or -173° C to 427° C). Lead melts at 600 kelvins! This large range in surface temperature is possible because
Mercury is so close to the Sun (a year is only 88 Earth days long) and does
not have sufficient atmosphere present to moderate the range in surface
temperature.
You might also be interested in:
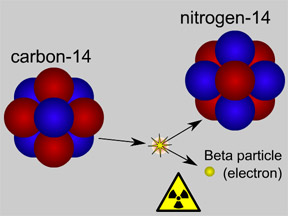
Some materials are radioactive. They emit radiation. When an atom of a radioactive substance emits radiation, it is transformed to a new type of atom. This process is called radioactive decay. There are
...more
Meteors are streaks of light, usually lasting just a few seconds, which people occasionally see in the night sky. They are sometimes called "shooting stars" or "falling stars", though they are not stars
...more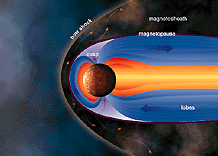
Mercury is the only terrestrial planet other than the Earth that has a significant magnetic field (220 nT). This field, along with the planet's high density and small size relative to the Earth, indicates
...more
Even though we can't see air, it is real and is made of up many molecules which are zipping around at astonishing speeds. Air molecules travel about 1,090 mph at the surface of the Earth. That said, all
...more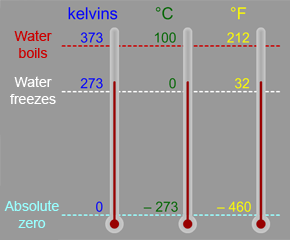
The Kelvin scale is a temperature scale that is often used in astronomy and space science. You are probably more familiar with the Celsius (or Centigrade) scale, which is part of the metric system of measures,
...more
The MErcury Surface Space ENvironment, GEochemistry Ranging mission
...more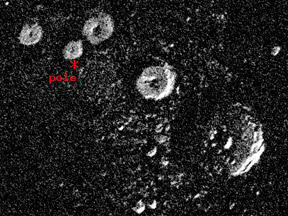
If Uranus is the "tilted planet", Mercury might be called the "upright planet". The spin axis of Uranus, which defines the locations of the planet's North and South Poles, is tilted by 98°. The spin axis
...more