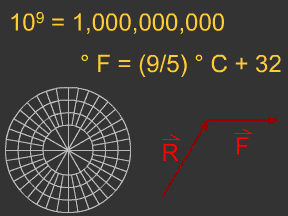Relativity - Time Dilation
This movie explains the concept of "time dilation", which is part of Einstein's theory of relativity.
Image courtesy of Trent Schindler, National Science Foundation. |
This movie explains an idea called "time dilation". Time dilation is an important part of Albert Einstein's theory of relativity. Imagine two people who are moving very, very fast relative to each other. Each of them will think that time is passing more slowly for the other person than it is for herself or himself. In other words, they will think the other person's clocks are running more slowly. Pretty strange, huh? That is just one of the very odd things that Einstein's theory of relativity says is true!
(Note: If you cannot see the movie you may need to download the latest QuickTime player.)
You might also be interested in:
Some ideas are used throughout the sciences. They are "tools" that can help us solve puzzles in different fields of science. These "tools" include units of measurement, mathematical formulas, and graphs.
...more
Some ideas are used in many, many places throughout science. We have grouped these "starting points for science" into three clusters: space, time, and matter. "Space" is the word we use for everything
...more
Some scientific problems and processes are so complex that you need SUPERCOMPUTING power to tackle them! Just what is a supercomputer? A supercomputer is a computer that is among the largest, fastest or
...more
In the last decades, computers have become a normal part of life. They are used to send e-mail, write a school report or look up recipes. They are used to keep track of the balance in your bank account.
...more
When it is noon where you live, it is midnight on the opposite side of the world. Usually when we think of time, we mean "the time of day where I live". If we say something happened at 9 AM, we mean it
...more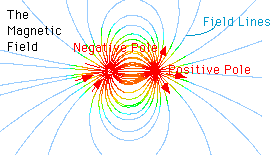
The force of magnetism causes material to point along the direction the magnetic force points. As shown in the diagram to the left, the force of magnetism is illustrated by lines, which represent the force.
...more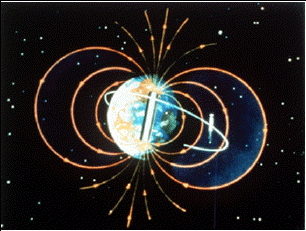
The Earth is a good example of a planetary dipole, where the lines of force point in a direction out of the South (magnetic) Pole and into the North (magnetic) Pole. Planets can also show evidence of quadrupoles
...more