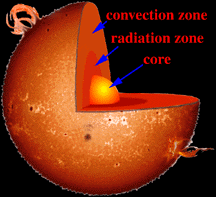
This diagram shows the structure of the Sun's interior. Two major regions inside the Sun, the convective zone and the radiative zone, are named for the way heat travels through them.
Click on image for full size
NASA
Thermal Physics
The scientific field of thermal physics is concerned with heat and temperature. When we delve into topics such as global warming, the structure
of Earth's solid and liquid cores, and the way in which energy flows from the
center of the Sun to its surface, we need an understanding of thermal physics.
Temperature is a familiar concept that is a cornerstone of thermal physics.
Three scales for measuring temperature are in common use: Fahrenheit, Celsius
(or Centigrade), and Kelvin. The temperature of a gas is actually a measure
of the average speed with which molecules or atoms are hurtling about. We infer
the temperatures of stars from their colors; hot stars are blue while cooler
ones are red.
In our everyday speech, heat and temperature are nearly synonymous. In the
language of thermal physics, the two terms have precise and quite different
meanings. Heat is essentially the amount of thermal energy stored within an
object.
Heat can flow from one object to another, transferring energy in the process.
The flow of heat can melt ice or warm the surfaces of planets near a star. The Laws of Thermodynamics
describe the fundamental physics of heat and its flows.
Heat tends to flow from hot places to cold ones, and often drives the motions
of other materials. Convection and conduction are two common ways by which
heat can flow. Electromagnetic radiation, especially at infrared wavelengths,
can convey heat across a vacuum. We study heat flows to understand the diffusion
of gases, the circulation of ocean currents, the outflow of energy from the
Sun, and the workings of rocket motors.
You might also be interested in:
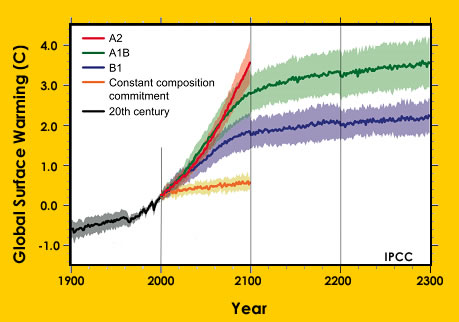
Earth’s climate is warming. During the 20th Century Earth’s average temperature rose 0.6° Celsius (1.1°F). Scientists are finding that the change in temperature has been causing other aspects of our planet
...more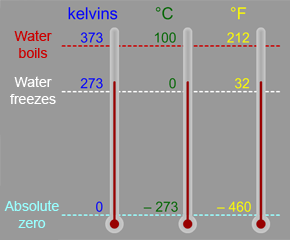
The Kelvin scale is a temperature scale that is often used in astronomy and space science. You are probably more familiar with the Celsius (or Centigrade) scale, which is part of the metric system of measures,
...more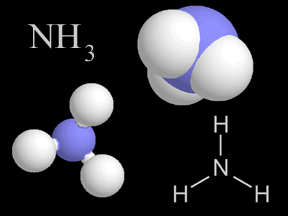
Most things around us are made of groups of atoms bonded together into packages called molecules. The atoms in a molecule are held together because they share or exchange electrons. Molecules are made
...more
The cryosphere includes the parts of the Earth system where water is in its frozen (solid) form. This includes snow, sea ice, icebergs, ice shelves, glaciers, ice sheets, and permafrost soils. Approximately
...more
Electromagnetic radiation is the result of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The wave of energy generated by such vibrations moves through space at the speed of light. And well it should... for
...more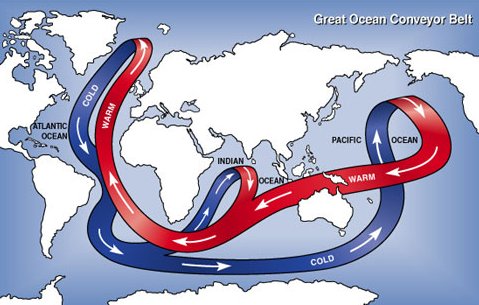
The world has several oceans, the Pacific, the Atlantic, the Indian, the Arctic, and the Southern Ocean. While we have different names for them, they are not really separate. There are not walls between
...more
Energy from the Sun is one of the primary drivers of the Earth system. The Sun warms our planet, heating the surface, the oceans and the atmosphere. This energy feeds atmospheric processes and is a primary
...more