Helium Ions (He II) in the Sun's Atmosphere
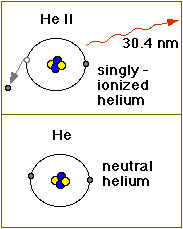 All stars are made up mostly of hydrogen and helium. Since atoms in the Sun's atmosphere are extremely hot, they move around very, very quickly. The atoms often collide, and such collisions can knock electrons loose from an atom. Atoms with missing (or extra!) electrons are called ions. A helium (chemical element symbol He) atom that is missing one electron is called He II. Normal, neutral helium atoms that still have both electrons are called He I. All stars are made up mostly of hydrogen and helium. Since atoms in the Sun's atmosphere are extremely hot, they move around very, very quickly. The atoms often collide, and such collisions can knock electrons loose from an atom. Atoms with missing (or extra!) electrons are called ions. A helium (chemical element symbol He) atom that is missing one electron is called He II. Normal, neutral helium atoms that still have both electrons are called He I.
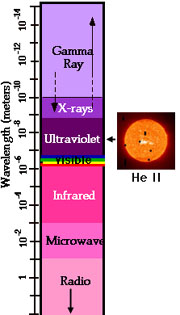
Under conditions (temperatures around 60,000 to 80,000 kelvins) that exist in the Sun's atmosphere, helium atoms are ionized to form He II ions. These ions emit extreme ultraviolet (EUV) radiation at a wavelength of 30.4 nm (304 Å). Radiation at this wavelength allows scientists to see structures and processes in the transition region - a special area in the Sun's atmosphere. The transition region is the boundary between the Sun's lower atmosphere (chromosphere) and its upper atmosphere (corona). These high energy UV emissions are (thankfully!) blocked by Earth's atmosphere, so scientists must use orbiting solar telescopes on satellites above the atmosphere to view the Sun at this wavelength.
Helium is a very rare element on Earth. Because it is lighter than air, helium is used to inflate balloons. Helium holds on to its electrons very strongly, making it extremely difficult to ionize. As a result of this, helium does not react easily with other chemicals. |
 |
You might also be interested in:
An element (also called a "chemical element") is a substance made up entirely of atoms having the same atomic number; that is, all of the atoms have the same number of protons. Hydrogen, helium, oxygen,
...more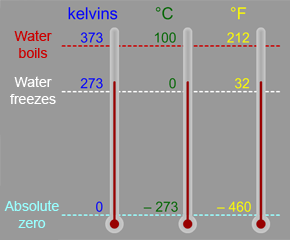
The Kelvin scale is a temperature scale that is often used in astronomy and space science. You are probably more familiar with the Celsius (or Centigrade) scale, which is part of the metric system of measures,
...more
Electromagnetic radiation is the result of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The wave of energy generated by such vibrations moves through space at the speed of light. And well it should... for
...more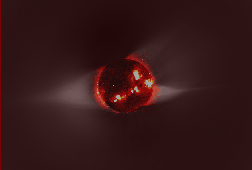
Rising above the Sun's chromosphere , the temperature jumps sharply from a few tens of thousands of kelvins to as much as a few million kelvins in the Sun's outer atmosphere, the solar corona. Understanding
...more
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is a satellite which carries several telescopes and other instruments for observing the Sun. The instruments on SDO produce much more detailed images than similar
...more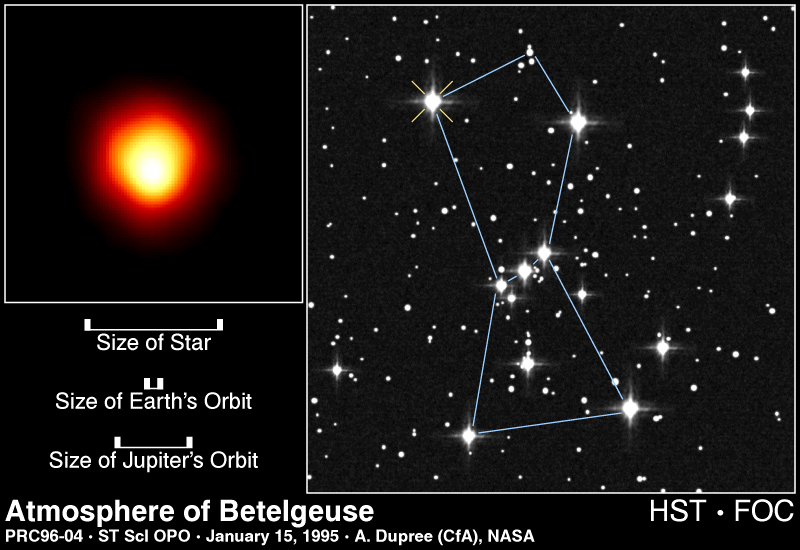
When the temperature in the core of a star reaches 100 million degrees Kelvin fusion of Helium into Carbon occurs (three Helium nuclei combine to form a nucleus of Carbon). In the same range of temperature
...more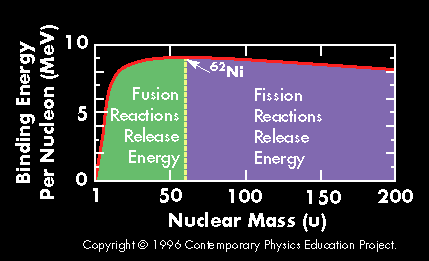
A plot of the binding energy per nucleon vs. atomic mass shows a peak atomic number 56 (Iron). Elements with atomic mass less then 56 release energy if formed as a result of a fusion reaction. Above this
...more



 All stars are made up mostly of hydrogen and helium. Since atoms in the
All stars are made up mostly of hydrogen and helium. Since atoms in the 











