Sir Arthur Eddington (1882-1944)
This image is in the public domain.
Sounds of the Stars
Sir Arthur Eddington is the author of a book called
The Internal Constitution of the Stars. He
wrote:
"At first sight it would seem that the deep interior of the sun and stars is less accessible... than any other region of the universe.
What appliance can pierce through the outer layers
of a star and test the conditions within?" The answer to his question is now known. The
sounds of the stars.
Geologists use earthquakes to understand the interior of the earth. In a similar way, astronomers can learn about the insides of stars that
pulsate.
These pulsations are like very low sound waves moving through the star. If we could make the waves move a million times faster, we could hear the sounds of the stars!
Different types of stars would have different sounds. Making sounds like our own Sun is the nearby star alpha Centauri  (click to listen). A giant star like xi Hydrae
(click to listen). A giant star like xi Hydrae  has a deeper tone. A tiny white dwarf star like GD 358
has a deeper tone. A tiny white dwarf star like GD 358  plays the higher notes. One astronomer has even worked with a composer to create a unique kind of music from these sounds.
plays the higher notes. One astronomer has even worked with a composer to create a unique kind of music from these sounds.
You might also be interested in:

You may have heard of sunspots that sometimes dot the "surface" of the nearest star, our Sun. Well, other stars have spots too. They are called starspots and are relatively cool, dark regions on the visible
...more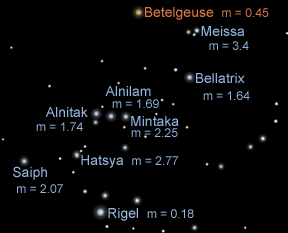
Astronomers use a special term to talk about the brightness of stars. The term is "magnitude". The magnitude scale was invented by the ancient Greeks around 150 B.C. The Greeks put the stars they could
...more
Because of the rotation of the Earth and its orbit around the Sun, we divide the stars and constellations into two groups. Some stars and constellations never rise nor set, and they are called circumpolar.
...more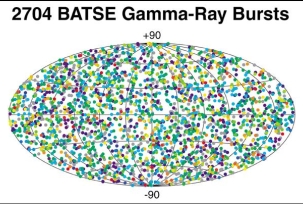
In the 1960's, the United States launched some satellites to look for very high energy light, called Gamma Rays. Gamma Rays are produced whenever a nuclear bomb explodes. The satellites found many bursts
...more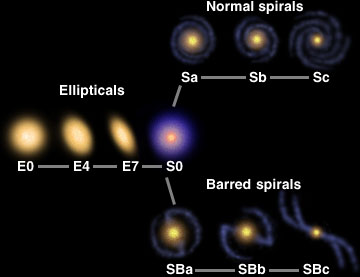
During the early 1900's, which is not very long ago, astronomers were unaware that there were other galaxies outside our own Milky Way Galaxy. When they saw a small fuzzy patch in the sky through their
...more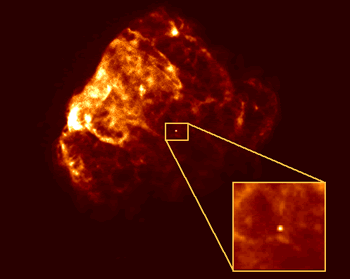
Neutron Stars are the end point of a massive star's life. When a really massive star runs out of nuclear fuel in its core the core begins to collapse under gravity. When the core collapses the entire star
...more
Spiral galaxies may remind you of a pinwheel. They are rotating disks of mostly hydrogen gas, dust and stars. Through a telescope or binoculars, the bright nucleus of the galaxy may be visible but the
...more

 (click to listen). A giant star like xi Hydrae
(click to listen). A giant star like xi Hydrae  has a deeper tone. A tiny white dwarf star like GD 358
has a deeper tone. A tiny white dwarf star like GD 358  plays the higher notes. One astronomer has even worked with a composer to create a unique kind of music from these sounds.
plays the higher notes. One astronomer has even worked with a composer to create a unique kind of music from these sounds.














