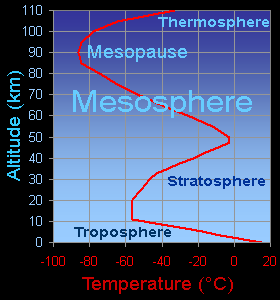
Temperatures decrease (get colder) with increasing altitude in the mesosphere.
Click on image for full size
Original artwork by Windows to the Universe staff (Randy Russell).
Temperature in the Mesosphere
Temperature decreases with height throughout the mesosphere. The coldest temperatures in Earth's atmosphere, about -90° C (-130° F), are found near the top of this layer.
The air is much thinner (less dense) in the mesosphere than in the stratosphere below. There are fewer air molecules, including ozone molecules which play such an important role in heating the stratosphere, to absorb incoming solar electromagnetic radiation.
Carbon dioxide in the mesosphere also helps make this layer cold. CO2 molecules absorb thermal energy (heat) from collisions with other molecules. The CO2 releases some of that energy as photons in a process called radiative emission. Some of those photons travel upward into space, effectively carrying heat away from the mesosphere.
You might also be interested in:
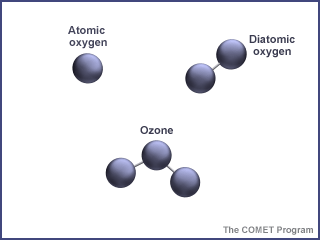
Ozone is a special kind of oxygen molecule. Normal oxygen molecules (O2), the kind we need to breathe, have two oxygen atoms. Ozone molecules (O3) have three oxygen atoms. Ozone forms when a photon of
...more
Electromagnetic radiation is the result of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The wave of energy generated by such vibrations moves through space at the speed of light. And well it should... for
...more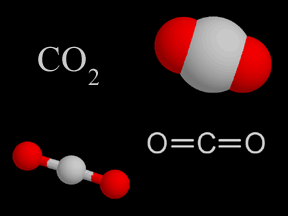
Carbon dioxide is a colorless and non-flammable gas at normal temperature and pressure. Although much less abundant than nitrogen and oxygen in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide is an important constituent
...more
Most things around us are made of groups of atoms bonded together into packages called molecules. The atoms in a molecule are held together because they share or exchange electrons. Molecules are made
...more
Rainbows appear in the sky when there is bright sunlight and rain. Sunlight is known as visible or white light and is actually a mixture of colors. Rainbows result from the refraction and reflection of
...more
The Earth travels around the sun one full time per year. During this year, the seasons change depending on the amount of sunlight reaching the surface and the Earth's tilt as it revolves around the sun.
...more
Scientists sometimes travel in specially outfitted airplanes in order to gather data about atmospheric conditions. These research aircraft have special inlet ports that bring air from the outside into
...more