Click on image for full size
US Minerals Management Service, Alaska Region
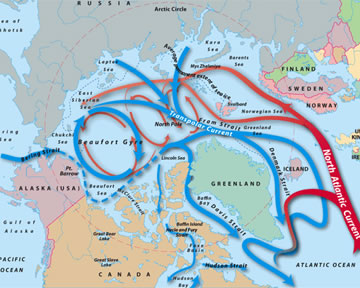
The Arctic: Earth's North Polar Region
North of the Arctic Circle (at 66.5°N latitude) you will find the Arctic Ocean surrounded by the continents of Europe, Asia, and North America. You will find the geographic North Pole and the magnetic North Pole there; both are in the Arctic Ocean, in an area that is currently covered year-round with sea ice. The aurora, called the Northern Lights in the Northern Hemisphere, can be visible in the night skies. Ice on the land is in glaciers. The Greenland ice sheet is the largest ice on land in the Northern Hemisphere. Most of the ice in the Arctic Ocean is called sea ice.
On the sea ice polar bears look for their favorite food, seals, which live in the Arctic Ocean. Other types of marine creatures live under the sea ice. On land, you will find a landscape where small plants and lichens grow even in harsh and cold conditions. This environment is called Arctic tundra. On the tundra, it is usually cold, often windy, and there is little precipitation. The soils are frozen most of the year. There are only a few species of mammals that can survive the harsh conditions of the tundra including reindeer (caribou) and arctic foxes. Many insect and bird species live in the Arctic tundra during the summer months, but migrate south during winter. Trees cannot grow in the tundra. Just south of Arctic tundra areas, the climate is slightly less cold and trees grow in taiga forests. In areas with taiga forests, temperatures get above freezing during the short summer.
Several cultures inhabit the lands that border the Arctic Ocean including various groups of Inuit people in coastal areas of northern North America, Greenland, and the Siberian region of Russia. People from Nordic countries, such as Sweden, Finland, Norway, Iceland, and Greenland, also inhabit lands that border the Arctic Ocean. People from Nordic countries are mainly descendants of the Norsemen or Vikings.