Space Shuttle Columbia Launches Succesfully
News story originally written on April 4, 1997
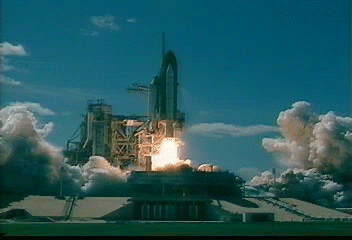
Space Shuttle Columbia lifted off today at 2:20 p.m. EST on a
16-day mission. Launch was delayed for a day due to concerns about a fuel
cell that was reading higher than normal voltages. After scientists
determined the fuel cell to be working properly, the countdown began.
The shuttle will orbit the Earth for two weeks at a height of 170 miles.
The mission consists of a microgravity lab which will study the behavior
of metals and other materials in the absence of gravity. The crew will
also study how no gravity affects combustion.
You might also be interested in:
Space Shuttle Columbia lifted off today at 2:20 p.m. EST on a 16-day mission. Launch was delayed for a day due to concerns about a fuel cell that was reading higher than normal voltages. After scientists
...more
Space Shuttle Columbia landed safely yesterday afternoon, cutting short the Microgravity Sciences Laboratory-1 by 12 days. The shuttle landed at Kennedy Space Center at 2:33pm. The Microgravity Science
...more
Very low levels of ozone were measured over the Arctic during March by several satellites. Ozone is a chemical that lies in the stratosphere and protects us from harmful solar radiation. Though the levels
...more
Scientists have recently discovered that thousands of Adelie Penguins thrive in patches of the chilly Southern Ocean near Antarctica's coastline. In these special areas of the ocean, called polynyas,
...more
Scientists have learned that Mount Hood, Oregon's tallest mountain, has erupted in the past due to the mixing of two different types of magma. "The data will help give us a better road map to what a future
...more
The Earth's mantle is a rocky, solid shell that is between the Earth's crust and the outer core, and makes up about 84 percent of the Earth's volume. The mantle is made up of many distinct portions or
...more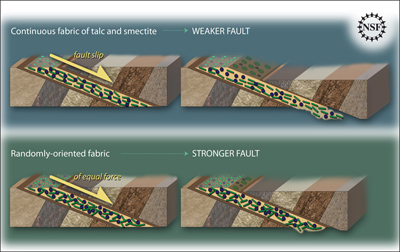
Some geologic faults that appear strong and stable, slip and slide like weak faults, causing earthquakes. Scientists have been looking at one of these faults in a new way to figure out why. In theory,
...more














