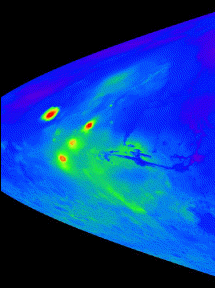
These images are maps of the surface of Mars, showing where the volcanos are located.
Click on image for full size
Image from: NASA
Does Mars have a surface in Motion?
Unlike Earth, there is no continental drift on Mars today. The Martian surface does not seem to have changed or moved in billions of years. The evidence for this fact can be found in two ways.
- 1.) The surface of Mars shows cratering at all latitudes and longitudes. Craters are wiped out when the surface of a planet moves. Since cratering stopped soon after the solar system formed, about 4 billion years ago, a surface which still shows evidence of that catering has not changed in a very long time.
2.) Mars has several very
large volcanoes. When the surface of a planet moves, volcanos are moved aside as well. They are worn down, and eventually
subducted below the surface. New volcanoes arise to take the place of the ones which have been swept away. The Martian volcanoes became as large as they are because there was no continental drift to recycle the surface on which they were built.
You might also be interested in:

The largest volcano in the solar system is Olympus Mons, shown in the image to the left. Olympus Mons is a Martian shield volcano. The altitude of Olympus Mons is three times the altitude of the largest
...more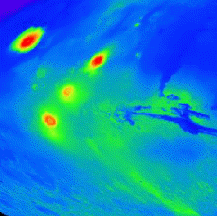
On this map of Mars, the lightly cratered Tharsis Ridge is shown, as well as the heavily cratered Martian highlands (near the bottom of the picture), and Valles Marineris to the right. The volcanoes are
...more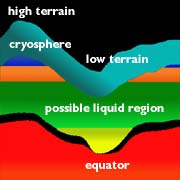
On Mars, the water is trapped, frozen, within the ground. Nevertheless, there is evidence for running water on Mars. When the water is melted and released to the surface, it will run from higher ground
...more
The drawing shows a crossection of the crust, and the unusual altitude variation of the Martian surface. The figure illustrates the depth of frozen ground at various latitudes, called the cryosphere. The
...more
Separate from the Martian outflow channels, or the river valley networks, are large Martian lakes (600 km, or ~1000 miles across) which exhibit evidence of a periodic and catastrophic release of water
...more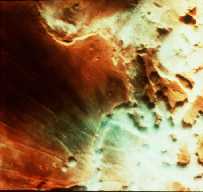
This is an image of fog in a Martian canyon. The presence of fog provides evidence of water, and a water cycle on Mars. More fog has been seen in images returned by Mars Global Surveyor of the south polar
...more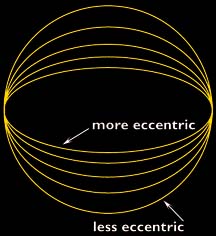
The Martian climate is more influenced by the shape of the Martian orbit than the climate of the Earth is influenced by the shape of the Earth's orbit. The orbit of Mars is more oval-shaped than that
...more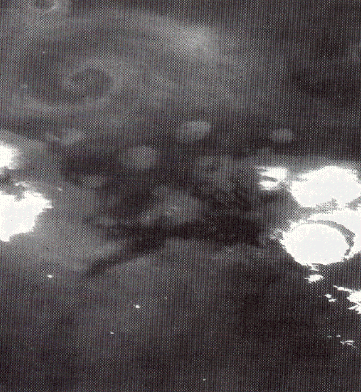
This is an image of a storm moving across the Martian terrain. The camera is looking down upon the storm and the storm front forms a spiral pattern, the same way terrestrial storms are presented on the
...more