Calcium Ions (Ca II K) in the Sun's Atmosphere
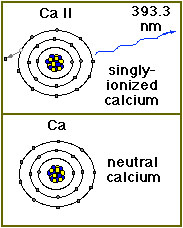 Calcium exists in small amounts in the solar atmosphere. Since atoms in the Sun's atmosphere are extremely hot, they move around very, very quickly. The atoms often collide, and such collisions can knock electrons loose from an atom. Atoms with missing (or extra!) electrons are called ions. A calcium (chemical element symbol Ca) atom that is missing one electron is called Ca II. Normal, neutral calcium is called Ca I. Calcium exists in small amounts in the solar atmosphere. Since atoms in the Sun's atmosphere are extremely hot, they move around very, very quickly. The atoms often collide, and such collisions can knock electrons loose from an atom. Atoms with missing (or extra!) electrons are called ions. A calcium (chemical element symbol Ca) atom that is missing one electron is called Ca II. Normal, neutral calcium is called Ca I.
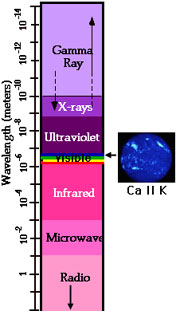
Under conditions (temperatures around 10,000 kelvins) that exist in the Sun's upper photosphere and chromosphere, calcium loses 1 electron and becomes singly-ionized (Ca II). It then gives off light in the visible or near ultraviolet range at 393 nm (3,933┼). Light at this wavelength is extremely faint but when the brilliant photospheric emissions are filtered out, the Ca II K line provides important information on the large-scale magnetic field structure in the chromosphere.
On Earth, calcium is a common gray metal that is found in chalk, limestone and the shells of mollusks. It is also crucial to the functioning of living organisms. It is essential for the growth of teeth and bones, helps control blood clotting and is used in transmitting messages along the body's nervous system. |
 |
You might also be interested in:
An element (also called a "chemical element") is a substance made up entirely of atoms having the same atomic number; that is, all of the atoms have the same number of protons. Hydrogen, helium, oxygen,
...more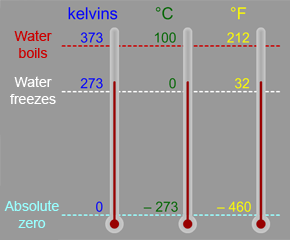
The Kelvin scale is a temperature scale that is often used in astronomy and space science. You are probably more familiar with the Celsius (or Centigrade) scale, which is part of the metric system of measures,
...more
Most of the energy we receive from the Sun is the visible (white) light emitted from the photosphere. The photosphere is one of the coolest regions of the Sun (6000 K), so only a small fraction (0.1%)
...more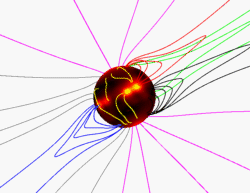
The Sun has a very large and very complex magnetic field. The magnetic field at an average place on the Sun is around 1 Gauss, about twice as strong as the average field on the surface of Earth (around
...more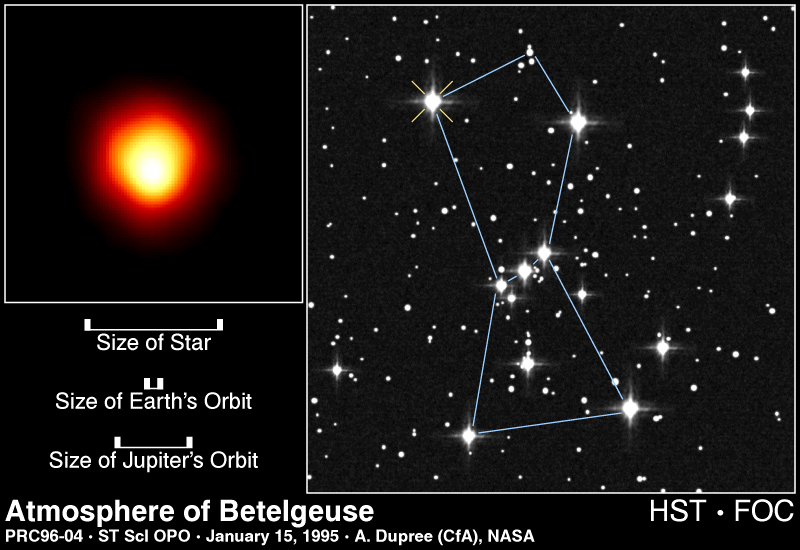
When the temperature in the core of a star reaches 100 million degrees Kelvin fusion of Helium into Carbon occurs (three Helium nuclei combine to form a nucleus of Carbon). In the same range of temperature
...more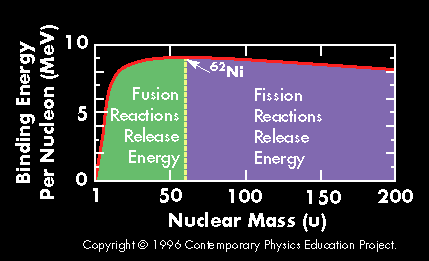
A plot of the binding energy per nucleon vs. atomic mass shows a peak atomic number 56 (Iron). Elements with atomic mass less then 56 release energy if formed as a result of a fusion reaction. Above this
...more
There are several experiments worldwide where the conditions for nuclear fusion reactions have been achieved in a controlled manner. The two main approaches that are being explored are magnetic confinement
...more



 Calcium exists in small amounts in the
Calcium exists in small amounts in the 











