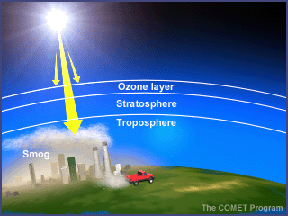
In the troposphere, the ground-level or "bad" ozone is an air pollutant that damages human health, vegetation, and many common materials. It is a key ingredient of urban smog. In the stratosphere, we find the "good" ozone that protects life on earth from the harmful effects of the Sun's ultraviolet rays.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of COMET program
Ozone - An Overview
The Ozone Hole. The Ozone Hoax. Pollution. Skin Cancer. The topic of ozone makes
headlines on a regular basis, but why does a single molecule merit such media
coverage? How important is the ozone in our atmosphere and why are scientists
so concerned about its increase near the surface of the Earth and its disappearance
higher up in the atmosphere?
First things first - what is ozone? Ozone is made of three oxygen atoms (O3).
The oxygen in our atmosphere that we breathe is made up of two
oxygen atoms (O2). Because of its chemical formulation, a single
atom of oxygen (O) is unstable. That is, it wants to combine with something
else. That is why oxygen is almost always found in pairs, in its (diatomic)
form, where it is more stable. (O3) is less stable than (O2),
because it wants to return to the diatomic state by giving up an oxygen atom.
When enough ozone molecules are present, it forms a pale blue gas. Ozone has
the same chemical structure whether it is found in the
stratosphere or the
troposphere. Where we find ozone in the atmosphere determines whether we
consider it to be Dr. Jekyll or Mr. Hyde.
In the troposphere, the ground-level or "bad" ozone
is an air pollutant that damages human health, vegetation, and many common materials.
It is a key ingredient of urban smog. In the stratosphere,
we find the "good" ozone that protects life on Earth from the harmful effects
of the Sun's ultraviolet rays. We have good reason to be concerned about the
thinning of the ozone layer in the stratosphere. We also have good reason to
be concerned about the buildup of ozone in the troposphere. Although simplistic,
the saying "Good up high and bad near by," sums up ozone in the atmosphere.
You might also be interested in:
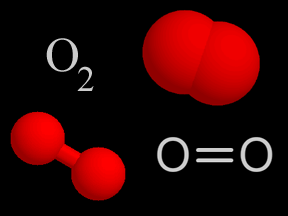
Oxygen is a chemical element with an atomic number of 8 (it has eight protons in its nucleus). Oxygen forms a chemical compound (O2) of two atoms which is a colorless gas at normal temperatures and pressures.
...more
What do smog, acid rain, carbon monoxide, fossil fuel exhausts, and tropospheric ozone have in common? They are all examples of air pollution. Air pollution is not new. As far back as the 13 th century,
...more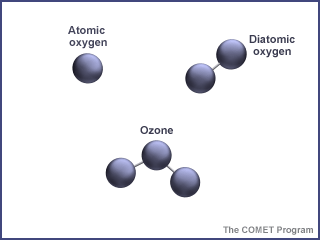
Ozone is a special kind of oxygen molecule. Normal oxygen molecules (O2), the kind we need to breathe, have two oxygen atoms. Ozone molecules (O3) have three oxygen atoms. Ozone forms when a photon of
...more
About 90% of the ozone in the Earth's atmosphere lies in the region called the stratosphere which is found between 16 and 48 kilometers (10 and 30 miles) above the Earth's surface. Ozone forms a kind of
...more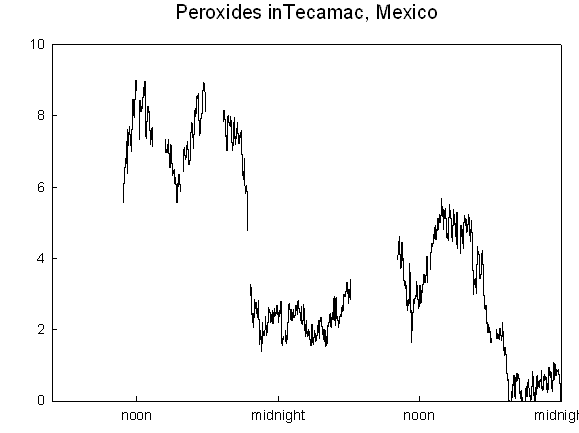
Hello again: We are nearing the end of our field campaign in Mexico. It has been a real adventure, with friendly people, great food, and interesting science. I obtained some good hydrogen peroxide measurements
...more
Television weather forecasts in the space age routinely feature satellite views of cloud cover. Cameras and other instruments on spacecraft provide many types of valuable data about Earth's atmosphere
...more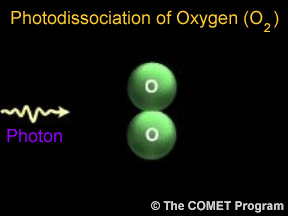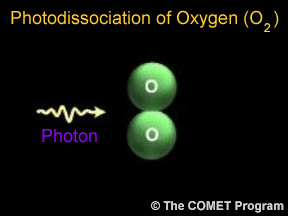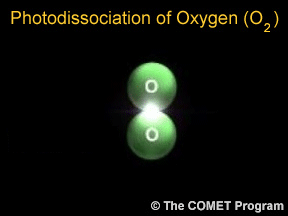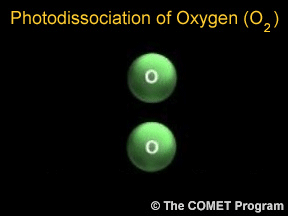
Sometimes when a photon hits a molecule, the energy from the photon causes the molecule to break apart. Scientists use the term "photodissociation" for such events. Photodissociation plays a very important
...more