Click on image for full size
Lisa Gardiner / Windows to the Universe
Earth's Greenhouse Effect
Energy from the Sun can enter the atmosphere, but not all of it can easily find its way out again. This is a natural process called the greenhouse effect. Without any greenhouse effect, Earth’s temperature would be below freezing. However, Earth’s greenhouse effect is intensifying as we add more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. This is warming the climate of our planet.
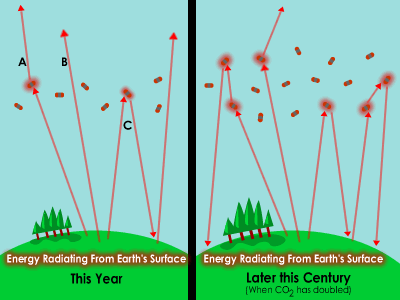
When sunlight warms the Earth’s surface, the heat is then radiated to the atmosphere. Some of this heat makes its way out of the Earth system – back to space - but along the way much of the heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases are more complex than most other gas molecules in the atmosphere, with a structure that can absorb heat. They radiate the heat back to the Earth's surface, to another greenhouse gas molecule, or out to space.
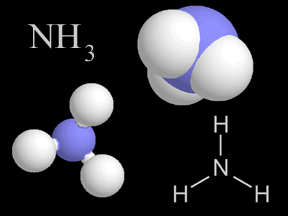
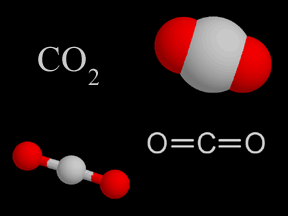
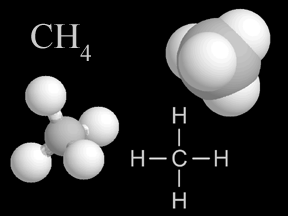
Sometimes during this Century, the amount of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide is expected to double. Other greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide are increasing as well. The amounts of greenhouse gases are increasing as fossil fuels are burned, which releases greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases also make their way to the atmosphere from other sources. Farm animals, for example, release methane gas as they digest food. Greenhouse gases are released as cement is manufactured, both from burning of fossil fuels to heat limestone to a high temperature, and from the creation of lime and carbon dioxide as the limestone is heated.
As forest trees are harvested for their wood, and land is converted to farms or urban center, there are less large trees to, through photosynthesis, take carbon dioxide out of the air. Potted plants, lima bean plants, grass – all types of plants do photosynthesis, but trees, and especially large trees, are very efficient at it.
With more greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, heat on its way out of the atmosphere is more likely to be intercepted. The additional greenhouse gases absorb the heat and then radiate it away from the Earth, to another greenhouse gas molecule, or back to the planet’s surface again. With more greenhouse gases, the atmosphere will radiates heat from a higher level, so less heat gets out. With more greenhouse gases, heat will get stuck in the system, warming the planet.