Video courtesy of the NSF.
Study Past Climate to Predict Future
Climate scientists use "proxy data" to study climates of the past, before humans with thermometers began keeping temperature records. These "proxies" include tree rings, layers within ice cores pulled from glaciers and ice sheets, growth layers in coral, and layers of sediments from the bottoms of lakes and oceans.
Studies of past climates help us anticipate how Earth's climate may change in the coming decades as a result of global warming. Climate scientists are especially interested in previous "interglacial" (between ice ages) climates, when Earth was warm. The scientists seek to determine how high temperatures rose, how quickly the climate changed, and which parts of the globe warmed most and least.
Human influences on climate have already committed us to at least several decades of warming in the coming century. The better we can anticipate how our climate may change, the better equipped we will be to adapt to those changes. Studies of past climates help us more fully understand the changes we are seeing today and can expect in the coming years.
Right-click (Windows) or Option-click (Mac) here to download a copy of this video in QuickTime format.
You might also be interested in:

For a glacier to develop, the amount of snow that falls must be more than the amount of snow that melts each year. This means that glaciers are only found in places where a large amount of snow falls each
...more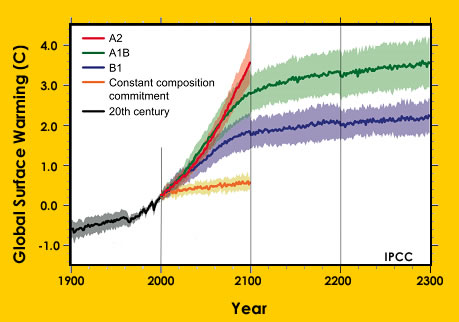
Earth’s climate is warming. During the 20th Century Earth’s average temperature rose 0.6° Celsius (1.1°F). Scientists are finding that the change in temperature has been causing other aspects of our planet
...more
A new report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) highlights how natural environments and human communities are coping with changing climate, how vulnerable they are, and whether they
...more
Leaders from 192 nations of the world are trying to make an agreement about how to limit emissions of heat-trapping greenhouse gases, mitigate climate change, and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
...more
Climate in your place on the globe is called regional climate. It is the average weather pattern in a place over more than thirty years, including the variations in seasons. To describe the regional climate
...more
Less than 1% of the gases in Earth's atmosphere are called greenhouse gases. Even though they are not very abundant, these greenhouse gases have a major effect. Carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O),
...more
Television weather forecasts in the space age routinely feature satellite views of cloud cover. Cameras and other instruments on spacecraft provide many types of valuable data about Earth's atmosphere
...more














