Click on image for full size
L.Gardiner/Windows to the Universe
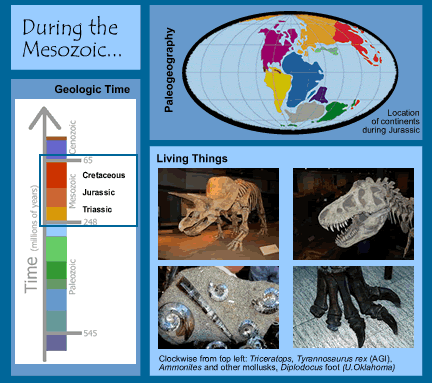
Happenings During the Mesozoic Era (248-65 Million Years Ago)
Time:248 to 65 million years ago
Geologic periods (divisions) of the Mesozoic: Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous
(See the geologic timescale!)
Paleogeography:
At the start of the Mesozoic, the continents were all together in a supercontinent
called Pangaea. Throughout the Mesozoic, they pulled apart from one another.
A narrow version of the Atlantic Ocean developed as ocean crust was formed at
the mid-Atlantic ridge. Continents move due to plate tectonics.
Climate:
- The climate most likely remained warm throughout the Mesozoic. There is no geologic evidence of glaciations and abundant fossil evidence of tropical species have been discovered.
- During the first part of the Cretaceous period (late Mesozoic) there is evidence that the climate warmed greatly and was warmer than it is today. Regional climate variations were negligible. There was little temperature variation between the equator and poles.
- There is strong evidence that relatively sudden climatic cooling occurred at the end of the Mesozoic as a result of either a massive asteroid impact near the Yucatan Peninsula, extensive volcanism in the area that is today India and Pakistan, or the combined effects of both events. The asteroid may even have been large enough to cause the volcanism, or the events may have just happened coincidentally at about the same time. The Sun would have been blocked for some time by debris sent into the atmosphere by the impact and eruptions, cooling the planet.
Evolutionary Events:
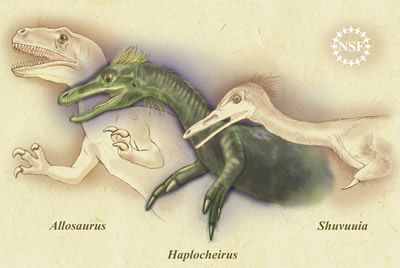
- Dinosaurs evolved in the Triassic and became abundant by the middle of the Mesozoic. Dinosaurs were reptiles, however there is evidence that they may have been warm-blooded.
- Birds: During the late Mesozoic, birds most likely evolved from a group of small carnivorous dinosaurs called theropods.
- Plants: Conifer trees evolved at the beginning of the Mesozoic. The first flowering plants evolved during the Cretaceous.
- Mammals evolved during the Mesozoic but there were relatively few species and they were small in size. During the Mesozoic, mammals were most likely food for predatory dinosaurs.
- At the end of the Mesozoic, the Cretaceous Tertiary Mass Extinction occurred.
This was the extinction event that killed the dinosaurs (among others). Many
of the animals and plants that survived (such as mammals and birds) went on
to become very abundant afterward in the Cenozoic. Likely causes of the extinction
event include one or more large asteroid impacts, widespread volcanism, and
climate change. There is evidence that all three of these happened.