Click on image for full size
Windows to the Universe original artwork by Randy Russell using images courtesy NASA/JPL.
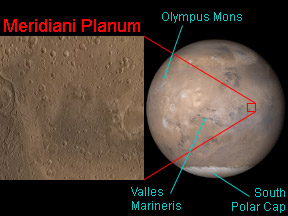
Meridiani Planum location on Mars
Meridiani Planum is a small, flat region near the equator on Mars. As is the case on Earth, locations on Mars are specified by stating their latitude and longitude. Meridiani Planum is near the prime meridian, the arbitrarily chosen location of the 0° longitude line, on Mars; hence the name "Meridiani". "Planum" means "plain", and Meridiani Planum is indeed a flat area.
Meridiani Planum is the location of the largest known concentration on Mars of the mineral gray hematite. On Earth, hematite deposits usually indicate that water was present in an area for long periods. Scientists are interested in Meridiani Planum because of the possibility that it could provide clues about the history of water in Mars' past. Meridiani Planum was chosen as the landing site for the second Mars Exploration Rover, named Opportunity, because of the chance that evidence for water might be found there.
An area called Margaritifer Terra, which is the easternmost end of the vast Valles Marineris canyon, is located just west of Meridiani Planum. Margaritifer Terra is a jumbled landscape that looks very much like the scene of large scale flooding. Chryse Planitia, northwest of Meridiani Planum, has many features that seem to indicate water flowed in that area as well. Meridiani Planum is on the boundary between Mars' southern highlands and its northern lowland plains. If Mars ever had oceans covering those northern lowlands, Meridiani Planum might have been a shallow area within them similar to the continental shelves of Earth's seas. There are many reasons to think that Meridiani Planum is a good place to look for evidence of water in Mars' past.