Readings: Climate Discovery Online Course for the ASTC C3 Community
 |
This resource page is for science educators from ASTC C3 partnering institutions who wish to explore readings and other web-based media from the Climate Discovery online course designed by UCAR's Office of Education and Outreach especially for ASTC.
This course guides participants through the basics of climate science and the impacts of recent warming to help informal educators be better prepared to answer common questions about climate. We explore climate and global change with an Earth system science perspective, describing the interactions between the various parts of the Earth system, including human activities, to learn how they affect our climate and how warming affects the Earth.
Note that these links to readings are not the complete course. There are other readings from the required text, self assessment quizzes, hands-on activities, discussions, and homework assignments on the MOODLE course page. |
WEEK 1: What Is Climate? How Do We Study It?
Climate is the average of weather conditions over a period of many years. It is studied in many ways.
|
|
WEEK 2: Past and Future Climate
Scientists study what climate was like in the past and predict how climate may change in the future.
|
|
WEEK 3: Regional Weather and Climate, and the Greenland Ice Case Study
Climate change is having different impacts in different regions. The Arctic is warming faster than other regions.
|
|
WEEK 4: Impacts on Urban Environments and Human Health
Climate change and other types of global change are having an impact on people, urban areas, and human health.
|
|
WEEK 5: Impacts of Climate Change on Land Plants and Coral Reef Ecosystems
Plants, animals, and ecosystems are affected by climate change.
|
|
WEEK 6: Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation
People around the world are making changes to the way they live that help adapt to, and mitigate, climate change.
|
|
Last modified June 15, 2009 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

Climate in your place on the globe is called regional climate. It is the average weather pattern in a place over more than thirty years, including the variations in seasons. To describe the regional climate
...more
A factor that has an affect on climate is called a “forcing.” Some forcings, like volcanic eruptions and changes in the amount of solar energy, are natural. Others, like the addition of greenhouse gases
...more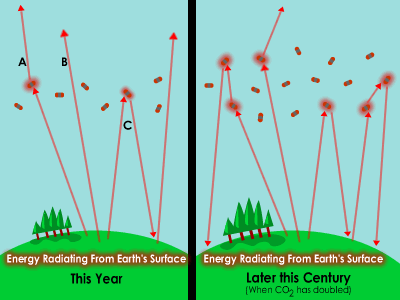
Energy from the Sun can enter the atmosphere, but not all of it can easily find its way out again. This is a natural process called the greenhouse effect. Without any greenhouse effect, Earth’s temperature
...more
Changes in the cryosphere have a considerable impact on global climate. This is because the cryosphere is an important part of the Earth system and because it is so interconnected with other parts of the
...more
Greenland, the enormous island – the world’s largest- that sits between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, is almost entirely covered with ice. A massive ice sheet blankets about 80% of the land surface.
...more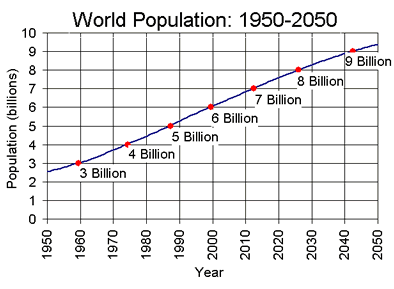
As of March 2008, the total number of human beings on the Earth is estimated to be more than 6.6 billion. The actual population is never known for certain, since these numbers rely on national censuses,
...more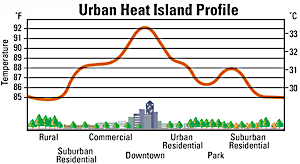
What Is an Urban Heat Island? An urban heat island (UHI) is a metropolitan area which is significantly warmer than its surroundings. According to the EPA, many U.S. cities have air temperatures up to 1
...more















