Astrophysical Objects Image List
Nebulae
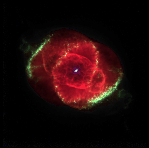
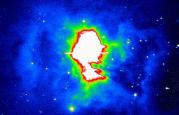
This image, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, shows a very complex planetary nebula. It is nicknamed the "Cat's Eye Nebula" and is about 1,000 years old. (Courtesy of NASA)
(113K GIF)
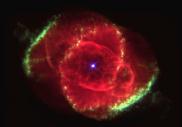
This is another image of the Cat's Eye Nebula.
(15K JPG)

This is the Trifid Nebula in Sagittarius. The red HII region with its young
cluster is surrounded by a blue reflection nebula. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(123K GIF)

This is the Cone Nebula in the NGC 2264 cluster. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(137K GIF)
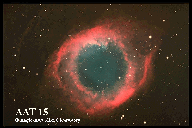
This is the Helix nebula, a planetary nebula in NGC 7293. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(111K GIF)

This is the Eagle nebula, surrounding the open cluster M 16, in NGC 6611. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(144K GIF)

This is the Horsehead Nebula and NGC 2023. (Courtesy Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(104K GIF)

This is the Tarantula Nebula around 30 Doradus. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(165K GIF)

This is an image of Antares & Rho Ophiuchi.
(56K JPG)

This is an image of the Horsehead Nebula which is 1500 light years.
(52K JPG)

This image shows a small portion of a nebula called the "Cygnus Loop." This supernova remnant lies 2,500 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus the Swan. (Courtesy of Jeff Hester (Arizona State University) and NASA)
(97K JPG)

This is an image of the Pleiades, an open cluster/reflection nebulae 400 light years away. It is easily seen with the naked eye and is known as the Seven Sisters.
(62K JPG)

This is an image of the Crab Nebula, a supernova remnant 6,000 light years away. Copyright Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy Inc. (AURA), all rights reserved.
(45K JPG)

This is an image of the Orion Nebula which is an emission nebula 1,500 light years away. It is known as "The Great Nebula of Orion."
(93K JPG)
This is an infrared cluster associated with NGC2024 nebula. (Image provided courtesy of Michael Meyer (meyer@mpia-hd.mpg.de))
(101K GIF)
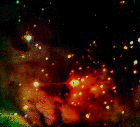
This is a newer version of the infrared cluster associated with NGC2024 nebula. (Image provided courtesy of Michael Meyer (meyer@mpia-hd.mpg.de))
(101K GIF)
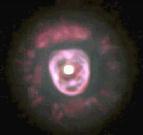
This is the Eskimo Nebula also known as Clownface Nebula which has an unusually bright central star.
(21K JPG)

This is the Keyhole Nebula which is 9,000 light years away.
(109K JPG)
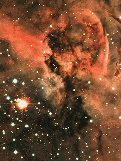
This is Eta Carinae and the Keyhole Nebula. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(146K GIF)

This is another image of Eta Carina. It is the largest diffuse nebula
(16K JPG)

This is the Trifid Nebula which is 2,000 light years away. It is called this because of the three dark division lanes. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(36K JPG)

This is the Lagoon Nebula, 4,500 light years away. It is much larger and brighter than its neighbor the Trifid Nebula and even visible with the naked eye on a dark night.
(101K JPG)

This is the Eagle Nebula, which is an emission nebula 7,000 light years away. There are many new stars formed here, but the nebula itself is much dimmer and harder to see than the nearby Omega Nebula.
(89K JPG)
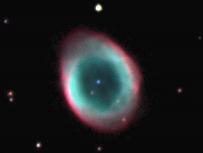
This is the Ring Nebula which is a planetary nebula 5,000 light years away. Its central star is very dim. Planetary nebulae are much smaller than diffuse nebulae and therefore more difficult to observe.
(20K JPG)
This is the Saturn Nebula, a planetary nebula 3,900 light years away. It gets its name because it resembles the planet Saturn.
(17K JPG)

This is the Vela Supernova Remnant. This nebula is the remnant of a supernova that exploded about 10,000 years ago.
(225K JPG)
Stars
This supernova, or exploding star, occurred in a type of galaxy called the starburst galaxy. They result from two galaxies that collide. (Courtesy of NASA)
(13K GIF)
This star image was taken on September 26, 1994 and located in the constellation of Andromeda about 200 million light years. (© WIYN Consortium, Inc.)
(64K GIF)
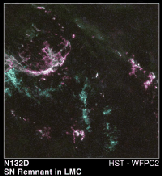
This is an oxygen rich supernova remnant in the large Magellanic cloud
(45K GIF)

This is an infrared image of the central section of the serpens star forming region
(60K GIF)
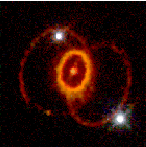
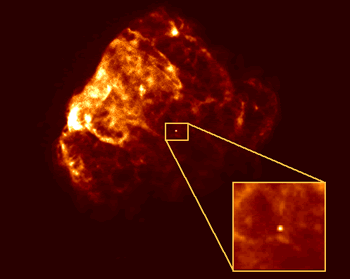
This image shows three rings of glowing gas encircling the site of supernova 1987A, a star which exploded in February 1987. (Courtesy of Dr. Christopher Burrows, ESA/STScI and NASA)
(100K GIF)

This image was taken on December 29, 1993 by the Hubble Space Telescope. It is a very young star surrounded by material left over from the star's formation. (Courtesy of C.R. O'Dell/Rice University and NASA)
(79K GIF)

Startrails around the South Celestial Pole. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(56K GIF)

A young open cluster, NGC 3293. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(37K GIF)

Startrails at Anglo Australian Observatory. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(73K GIF)

A Wolf-Rayet star in NGC 2359. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(70K GIF)

The Jewel Box cluster in Crux, NGC 4755. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(49K GIF)
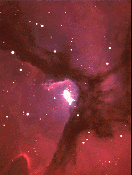
The stars that excite the Trifid Nebula. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(65K GIF)

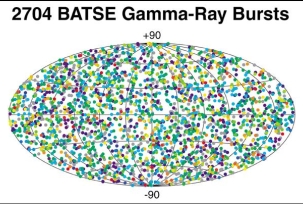
V-filter flux for stars
(183K GIF)

This is M67 in Cancer taken on April 25, 1995 at the Physics Department, Brown University, Providence, RI, USA. (Courtesy of Brown University)
(49K GIF)
Galaxies
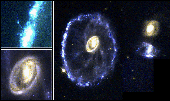
This Hubble Space Telescope true-color image is the Cartwheel Galaxy, located 500 million light-years away in the constellation Sculptor. (Courtesy of NASA)
(300K GIF)

This is another Hubble Space Telescope image. It is of the rich galaxy cluster Abell 2218. The arc in this image is an illusion caused by the gravitational field of the cluster. (Courtesy of NASA)
(270K GIF)

This Hubble Space Telescope image shows evidence for a merger between a quasar and a companion galaxy. (Courtesy of John Bahcall, Institute for Advanced Study, NASA)
(71K GIF)

A Hubble Space Telescope image of a spiral-shaped disk of hot gas in the core of active galaxy M87. The disk is rotating so rapidly it contains a massive black hole at its hub. (Courtesy of NASA)
(28K GIF)

Quasar's host galaxies (Courtesy of Dr. John Hutchings,Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, NASA)
(65K GIF)
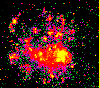
Large Magellanic Cloud
(234K GIF)

This is the Andromeda Galaxy, our nearest large neighbor galaxy.
(86K GIF)
More of Andromeda Galaxy
(54K GIF)

This is the The Triangulum galaxy M33. Under good conditions it can be seen with the naked eye.
(49K GIF)
This is the same thing but an ultraviolet image.
(74K GIF)
This is the same thing but a visible image.
(52K GIF)
This is the same galaxy of an ultraviolet and visible overlay.
(180K GIF)

This is the Whirlpool Galaxy M51 and was one of Messier's original discoveries.
He discovered it on October 13, 1773, when observing a comet.
(107K GIF)
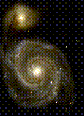
Another image of the Whirlpool Galaxy.
(72K GIF)

This is an image of the Spiral Galaxy M74.
(79K GIF)
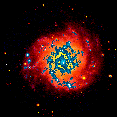
Another image of M74 with ultraviolet and visible overlay.
(152K GIF)
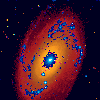
This is an image of the spiral galaxy M81 in Ursa Major with ultraviolet and visible overlay.
(143K GIF)
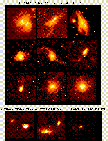
This is an example of the development of galaxy mergers.
(64K GIF)

This radio galaxy Centaurus A (NGC 5128) provides an example of how dust can affect our view of a galaxy, and how going to redder wavelengths helps penetrate interstellar dust.
(34K GIF)

Another image of Centaurus A. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(91K GIF)
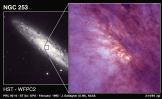
This is an image of NGC 253 (Courtesy of NASA)
(52K JPG)

These are images of NGC 1068.
(71K GIF)

This is a spiral galaxy, NGC 2997. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(115K GIF)

This is the Seyfert Galaxy, NGC 1566. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(69K GIF)

This is the Barred Sprial Galaxy, NGC 1365. (Courtesy of the Anglo-Australian Observatory/Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
(97K GIF)
Go back to Mars
, Jupiter,
Mercury,
Saturn,
Neptune,
Venus
,
Moon,
Earth,
Asteroids,
Comets,
Sun
,
Missions,
Uranus