Click on image for full size
Robert Wood (University of Washington) and the VOCALS Scientific Working Group
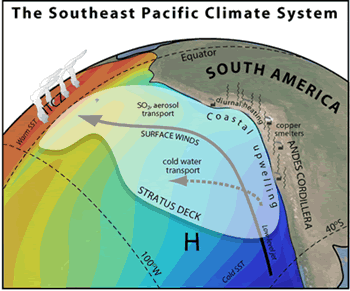
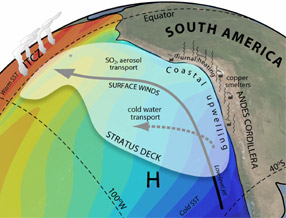
Southeast Pacific Climate
There are a lot of clouds over the Southeast Pacific Ocean off the coasts of Peru and Chile in South America. In fact, this area has the largest amount of stratus and stratocumulus clouds in the world! These important clouds are part of the Southeast Pacific climate system. Other important parts of the climate system in this area include the Southeast Pacific Ocean and the Andes Mountain Range. Scientists in the VOCALS field campaign are going to study this area so they can learn more about the Southeast Pacific Ocean.
The Andes Mountains form a pretty big barrier to the surface winds. flow parallel to the western coast of South America. The winds help bring deep, nutrient-rich waters to the surface. These cold waters help support the largest area of stratocumulus clouds found on the planet.
Strong winds from the west blow thousands of miles across the Pacific Ocean toward South America. When they reach land and run into the Andes Mountains, they are forced to turn north. The winds also push ocean surface water away from the coast to the west in a process scientists call Ekman transport. When the surface water is pushed west it is replaced by very cold water from deep in the ocean. This is known as upwelling.
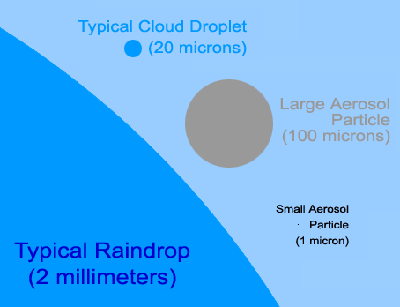
Most of the air over the Southeast Pacific Ocean is very clean. However, copper smelters located in Chile and Peru produce aerosols. Aerosols can also be found naturally in the Southeast Pacific region from sea salt and plankton. Aerosols are known to impact how clouds are formed.