Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NASA
Hurricanes (also known as Tropical Cyclones)
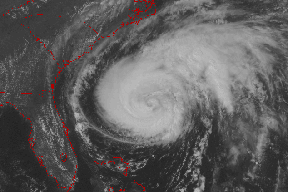
As a strong hurricane heads towards a vulnerable coast, people take precautions - boarding up houses, packing the car, and evacuating. These massive storms can spell disaster for people in hurricane prone areas, so they are taken seriously. They are the most powerful of all weather systems and they are huge - 340 miles in diameter on average.
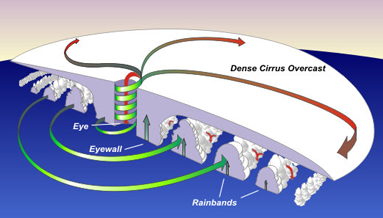
Hurricanes form in the tropics over warm ocean water and die down when they move over land or into higher latitudes. These storms are called hurricanes in the Atlantic and typhoons or tropical cyclones in other areas of the world. In the Northern Hemisphere the storms rotate counterclockwise and in the Southern Hemisphere they rotate clockwise due to the Coriolis Effect. At the center of the rotating storm is a small area of calm weather and clear skies called the eye. While the eye may be calm, the area directly around it - called the eyewall - is often the most dangerous part of the storm.
Hurricane damage in coastal areas is often due to storm surge, which floods coastal areas. Strong waves and wind also batter coastal areas. Hurricanes also cause a tremendous amount of rain. Not all storms are the same. Large and strong storms cause much more damage than small storms. Scales are used to describe the size of a hurricane. In the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific, the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale is used.
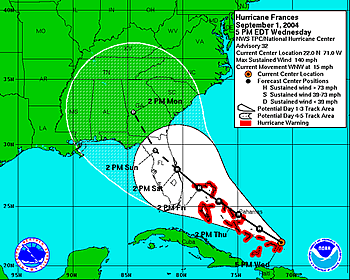
As hurricanes move, meteorologists try to forecast where and when the storm will reach land in order to warn people. Hurricanes are tracked over large distances with weather satellites. To forecast where the storm will go, meteorologists use computer models that take into account factors of the storm and the atmosphere. Since 1953 each hurricane has been given a name to help warn people that a storm was on its way.
In the North Atlantic, hurricanes typically happen between June 1st and November 30th. This is known as hurricane season. More hurricanes form in the North Atlantic between August and September than any other time of year. Other regions of the world have somewhat different timing of hurricane season, but in all areas the season overlaps with the summer months when the warmest temperatures fuel the powerful storms.