Click on image for full size
UCAR
What Is a Climate Model?
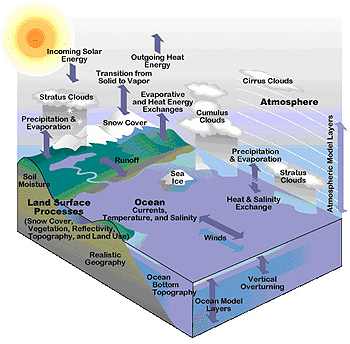
Global climate models use math - alot of math - to describe how the Earth works. They include math calculations about how the air, water, land, living things, and ice on Earth affect climate. They include math calculations about how the Sun's rays affects Earth's climate. Scientists use global climate models to better understand how changes like more greenhouses gases or less sea ice will affect our planet. With the models they look hundreds of years into the future to predict how our planet’s climate will likely change.
There are various types of climate models. Some focus on certain things that affect climate such as the atmosphere or the oceans. Others model the entire Earth. Their math calculations take into account as many parts of the planet as they can. Earth is a complex place and so many of these models are very complex too. They include so many math calculations that they must be run on supercomputers, giant and speedy computers which can do the calculations quickly. All climate models must make some assumptions about how the Earth works, but in general, the more complex a model, the more factors it takes into account, and the fewer assumptions it makes. At the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), researchers work with complex models of Earth's climate. Their largest model is so complex that it makes about three trillion math calculations to simulate a single day on planet Earth. It can take thousands of hours for the supercomputer to run the model. The model output is analyzed by researchers and compared with other model results and with observations.
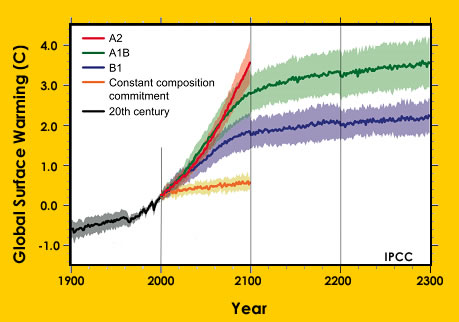
There are currently several other complex global climate models that are used to predict future climatic change. The most robust models are compared to help us understand future climate change.